Annuity (PV)- Solve for n
Solve for n - Annuity (PV) Calculator (Click Here or Scroll Down)
%201.gif)
The solve for n, or number of periods, formula shown above is used to determine the number of periods on an annuity using the present value, periodic payment, and periodic rate. An example of what the solve for n formula tries to answer is "How long will it take me to pay off a balance of $a at a rate of b% by making periodic payments of $c."
Example of Solve for n on Annuity (PV) Formula
An individual is attempting to determine how many payments would be needed if they offered someone $19660 at an effective rate of 1% per month. The periodic payment needed by the individual is $1,000 per month.
When considering this formula, it is important that the period used for the rate and payments match. For this example, the 1% rate and periodic payment is on a monthly basis. If the term and rate do not match on a 'per period' basis, then the effective rate would need to be found that matches how often the payments are received. The term "effective" in effective rate implies that compounding is already factored in. For example, if payments are annual, then the effective annual rate is used.
Using the solve for n on an annuity using present value formula, this example would be shown as
%202.gif)
The equation shown above for this example can then be reduced to
%203.gif)
After solving, the number of $1,000 payments needed is 22*.
* Please note this is for academic purposes only. The last payment will likely be more or less than the periodic payment depending on fees, the exact time payments are made, and other factors.
How is the Solve for n on Annuity (PV) Formula derived?
The formula for number of periods, n, on an annuity when present value is known can be found by first looking at the present value of an annuity formula.
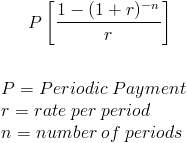
The number of periods, n, can be found by rearranging the present value of annuity formula shown above. First, both sides can be multiplied by -(r/P) followed by adding 1 to each side which leads to the equation
%204.gif)
From here, both sides can be taken to the power of -1 to isolate the right side to (1+r)n. To solve for exponent n requires using ln on both sides which results in the following equation
%205.gif)
Both sides can be divided by ln(1+r) which results in the formula at the top of the page.
Alternative Method for Solving for n on Annuity (PV)
Another way of finding the number of periods, or n, is the use of a present value of annuity table. The present value of annuity table is generally used to calculate the pv itself, but the number of periods can be found by using the table in reverse. By dividing pv by the payment (PV/P), the resulting number can be matched up in the "middle section" of the table to find the number of periods. Using the prior example, $19660 can be divided by periodic payments of $1000 which will result in 19.66. By using a present value of annuity table, one can see that 19.66 matched up with a periodic rate of 1% shows approximately 22 periods.
- Formulas related to Annuity (PV) - Solve for n
- PV of Annuity
- PV Annuity Factor
- Solve for n - Annuity (FV)
- Discounted Payback Period