Yield to Maturity
YTM Calculator (Click Here or Scroll Down)
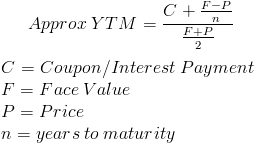
The yield to maturity formula is used to calculate the yield on a bond based on its current price on the market. The yield to maturity formula looks at the effective yield of a bond based on compounding as opposed to the simple yield which is found using the dividend yield formula.
Notice that the formula shown is used to calculate the approximate yield to maturity. To calculate the actual yield to maturity requires trial and error by putting rates into the present value of a bond formula until P, or Price, matches the actual price of the bond. Some financial calculators and computer programs can be used to calculate the yield to maturity.
Yield to Maturity and Present Value of a Bond
The yield to maturity is found in the present value of a bond formula:
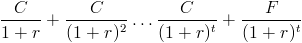
For calculating yield to maturity, the price of the bond, or present value of the bond, is already known. Calculating YTM is working backwards from the present value of a bond formula and trying to determine what r is.
Example of Yield to Maturity Formula
The price of a bond is $920 with a face value of $1000 which is the face value of many bonds. Assume that the annual coupons are $100, which is a 10% coupon rate, and that there are 10 years remaining until maturity. This example using the approximate formula would be
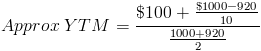
After solving this equation, the estimated yield to maturity is 11.25%.
Example of YTM with PV of a Bond
Using the prior example, the estimated yield to maturity is 11.25%. However, after using this rate as r in the present value of a bond formula, the present value would be $927.15 which is fairly close to the price, or present value, of $920. Other examples may have a larger difference.
A higher yield to maturity will have a lower present value or purchase price of a bond. In this example, the estimated yield to maturity shows a present value of $927.15 which is higher than the actual $920 purchase price. Therefore, the yield to maturity will be a little higher than 11.25%.
Through trial and error, the yield to maturity would be 11.38%, which is found by adjusting each estimated rate until the present value equals the price of the bond.
Excel is helpful for the trial and error method by setting the spreadsheet so that all that is required to determine the present value is adjusting a fixed cell that contains the rate.
- Formulas related to YTM
- Current Yield